Here’s when you need a stress test and what you can expect to learn from one
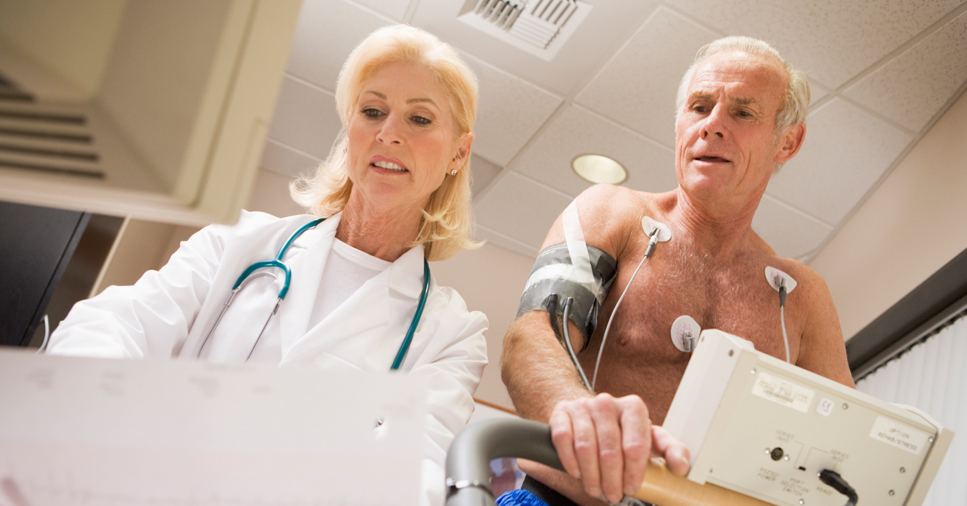
Your doctor gives you a stress test to see how your heart functions when it’s working during physical activity. You usually do it on a treadmill. The exercise makes your heart pump more blood to your body while you’re exercising. The test shows if there’s a problem with blood flow through your arteries.
There are three common types of stress tests:
- A dobutamine/adenosine stress test shows how your heart functions by giving you a drug to simulate your heart if you can’t exercise.
- A stress echocardiogram uses sound waves to create an image of your heart’s movement. This helps your doctor see the pumping action and blood flow while your heart is exerting energy.
- A nuclear stress test happens while you’re at rest and exercising. Your body has a small amount of radioactive dye injected. The dye flows through your heart and shows blockages or other problems on imaging tests.
Why would I need a stress test?
A doctor may recommend a stress test if you have possible symptoms of heart disease or other heart problems, including:
- Chest pain
- Irregular heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
You may also have a stress test if you’re starting an exercise program on your own or through a cardiac rehabilitation program.
What can stress tests help to find?
A stress test could find a significant blockage in a blood vessel leading to your heart. This means your heart can’t work as well as it should. A stress test can also find abnormalities with how your heart pumps blood during and after exercise. That may be a sign of coronary artery disease.
An echocardiogram may show if you’ve already had a small heart attack. It shows any weakened pumps or valves. It also shows the quality of the lining around your heart.
A nuclear stress test gives information about the blood flow to your heart. If there’s reduced blood flow, that’s a possible sign of a blocked artery.
What to expect during a stress test
A stress test is safe to take. Before your test, avoid caffeine for accurate results. During the test, you’re hooked up to an electrocardiography machine. You have electrodes on your skin that monitor your heart while you walk on a treadmill. The speed of the treadmill may change throughout the test. The test monitors numerous things, such as your heart rate, breathing, blood pressure and how tired you feel.
You can stop the test if you feel uncomfortable at any time. During the test, you may experience some chest pain, shortness of breath, blood pressure changes, dizziness or an irregular heartbeat. After you stop the test, you rest with the monitors still in place. After the stress test, you can go right back to your daily activities. The entire test can take around 30 to 45 minutes.
What do the results of a stress test mean?
A stress test on its own doesn’t always help your doctor get a definite diagnosis. Results often require follow-up testing. A stress test is a tool that can help your doctor figure out the next steps. The test can tell you if fatty deposits are blocking a blood vessel 70% or more, but you need more tests to confirm it. There are two results:
- Normal, which means you don’t have any blood vessels blocked more than 70% and there’s sufficient blood flow
- Abnormal, which means you may have a blood vessel blocked more than 70% and there’s insufficient blood flow
Even if you receive a normal result, you could have a future problem if a blockage grows.
If you’ve already been diagnosed with a heart disorder, a stress test can help guide your doctor in a treatment plan. The test results may help figure out the best timing for a valve replacement during heart surgery. The results could also tell a doctor if you need a heart transplant.
If you’re concerned about your heart health, we can help. Find a doctor near you, and we’ll help you make an appointment with a primary care doctor or heart specialist to learn more.